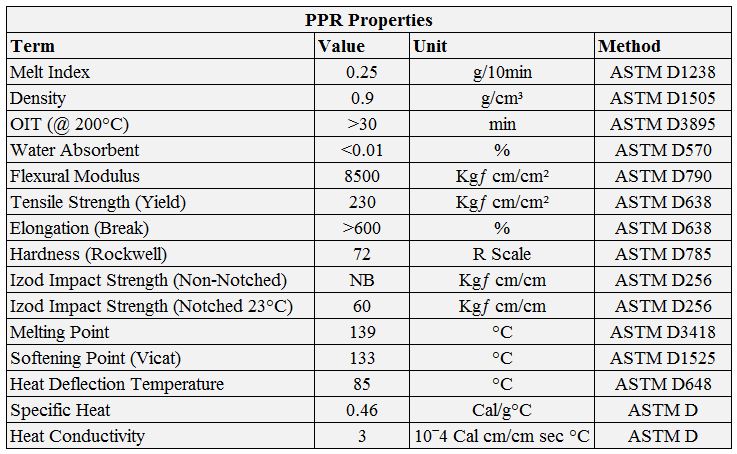
PP-R Properties

PPR pipe is a Pipe made of Polypropylene Random Copolymer (Polypropylene Random Copolymer type 3). The raw material used for this is Polypropylene Random Copolymer (PPR-C Type 3). PPR is highly resistant to alkalis and many acids, except for some highly concentrated acids. The inner smoothness of pipes prevents the formation of scale. Like all plastics, PPR is a poor heat conductor and is therefore an excellent thermal insulator.
Its properties can be seen in the table below.
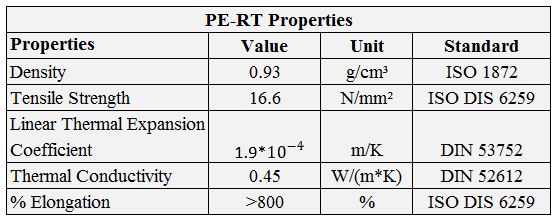
PE-RT Properties

PE-RT is a polyethylene (PE) resin in which the molecular architecture has been designed such that a sufficient number of tie chains are incorporated to allow operation at elevated or raised temperatures (RT). Tie chains “tie” together the crystalline structures in the polymer, resulting in improved properties such as elevated temperature strength and performance, chemical resistance and resistance to slow crack growth.

The pipes fabricated with PE-RT and evaluated according to the normative EN 921 at different temperatures (20, 60 80, 95 and 110 ºC) and pressures, using the extrapolation method of the EN ISO 9080, they present a curve of regression (or of reference) with surprising long life high resistance and high temperature. This widely surpasses a year of test at 110ºC and this allows to extrapolate the corresponding behavior at 70ºC and 50 years. Due to the little slope of the curve, the resistance values to 50 years result even very high.
PLA Properties

Polylactic Acid, commonly known as PLA, is one of the most popular materials used in desktop 3D printing. It is the default filament of choice for most extrusion-based 3D printers because it can be printed at a low temperature and does not require a heated bed. PLA is a great first material to use as you are learning about 3D printing because it is easy to print, very inexpensive, and creates parts that can be used for a wide variety of applications. It is also one of the most environmentally friendly filaments on the market today.
